Images: Vinehealth
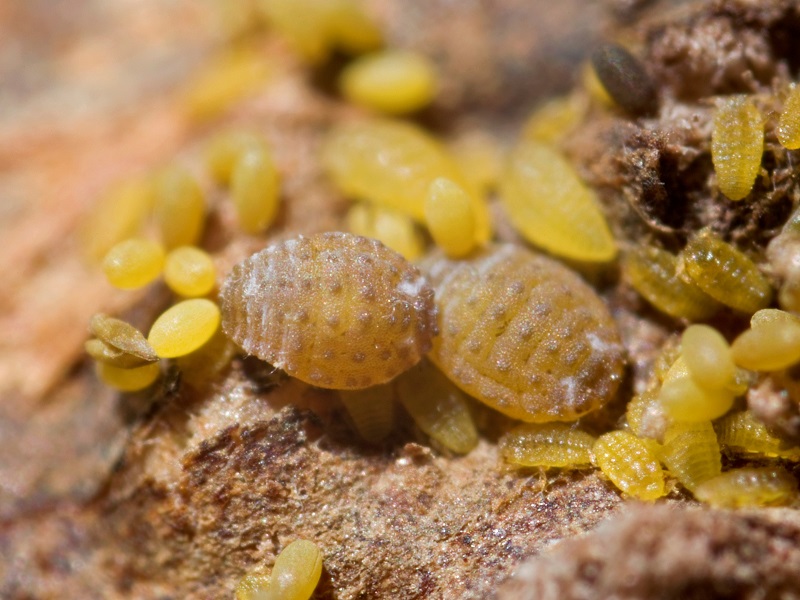
Vinehealth Australia, together with Wine Yarra Valley, is hosting 35 wine industry members in Victoria’s Yarra Valley today to see the impacts of the grapevine killer, phylloxera, firsthand.
The 2019 Phylloxera Immersion Tour will also allow participants to hear the latest science and learn how they can avoid infestation.
Phylloxera was first detected in the Yarra Valley in December 2006. The region’s Maroondah Phylloxera Infested Zone (PIZ) boundary has been redrawn seven times since then as new detections have been reported.

Rob Sutherland, viticulturist at De Bortoli Wines in the Yarra Valley, has estimated the financial impact of phylloxera in the Yarra Valley at about $1 billion, based on replanting nearly the whole region to rootstock and accounting for losses due to production lag.
This figure would rise further when other factors such as loss of brand continuity, business value and compliance costs are taken into account.
Vinehealth Australia CEO Inca Lee said the Phylloxera Immersion Tour was a valuable opportunity for members of the wine supply chain to educate themselves about the vine killer, which has been called the world’s worst agricultural pest.
“We know phylloxera doesn’t respect state borders. To prevent the introduction of phylloxera or other harmful pests and diseases, the wine industry’s commitment to biosecurity has never been more important,” Lee said.
“There are simple things growers and winemakers can do to stop the spread of pests and diseases that are being discussed throughout the tour.”
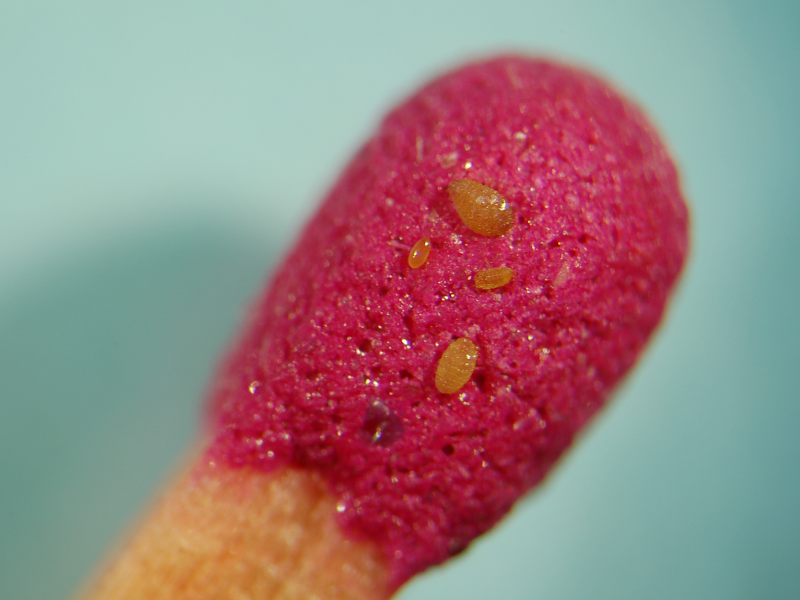
Phylloxera is a hitchhiker pest that is established in parts of Victoria and New South Wales and has previously been detected in Queensland, while South Australia, Western Australia and Tasmania are phylloxera free.
According to Vinehealth, there is no chemical or biological treatment for a phylloxera-infested vineyard. The only option is to pull out the vineyard and replant with new vines that have been grafted onto phylloxera tolerant or resistant rootstock.